跨物种单拷贝直系同源基因
同源(Homology)
同源(Homology) 的概念是这样定义的:
Homology:the existence of shared abcestry between a pair of strctures,or genes, in different species
如果两个或多个结构具有相同的祖先,也就是它们由一个共同祖先演化而来,则称它们同源(Homology)
在生物信息学中,同源主要指的是序列上的同源,即用来说明两个或多个蛋白质氨基酸序列或者DNA序列具有共同的祖先。同源的序列一般具有相似的功能,序列中同源的部分也称为保守的(conserved)
蛋白质和DNA的同源性常常根据它们序列的**相似性(Sequence similarity)来判定,相似性一般用检测序列和目标序列之间的序列一致性(Percent identity)**来表示
**相似性(Sequence similarity)**是指序列比对过程中用来描述检测序列与目标序列之间相同DNA或氨基酸残基所占比例。一般来说,相似程度高于50%则认为序列之间是同源序列
直系同源(orthology)与旁系同源(paralogy)
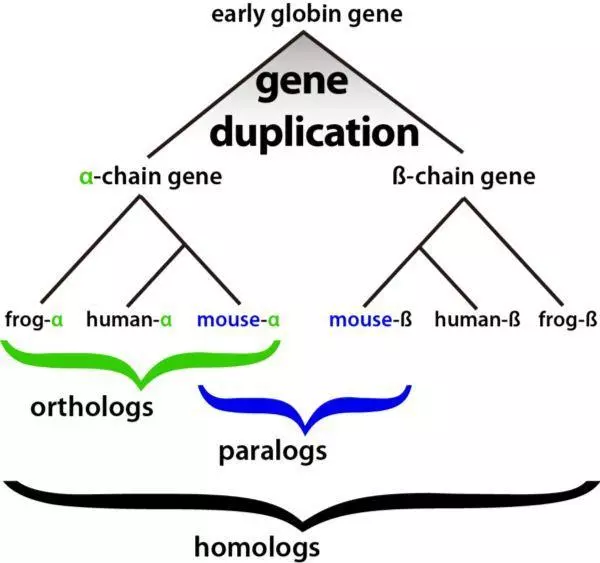
同源现象可分为直系同源(orthology)与旁系同源(paralogy)
Orthologys(orthology genes) are genes in dofferent pecies that originated by vertical descent from a single gene of the last common ancestor
**直系同源(orthology)**是指不同物种中的某一基因来自同一祖先,在演化过程中因物种形成(speciation)而被区分开来
Paralogys(paralogous genes) are created by a duplication event within the genome. For gene duplicationevents, if a gene in an organism is duplicated to occupy two different positions in the same genome, then the two copies are paralogous
旁系同源(paralogy)是指种系间的基因复制
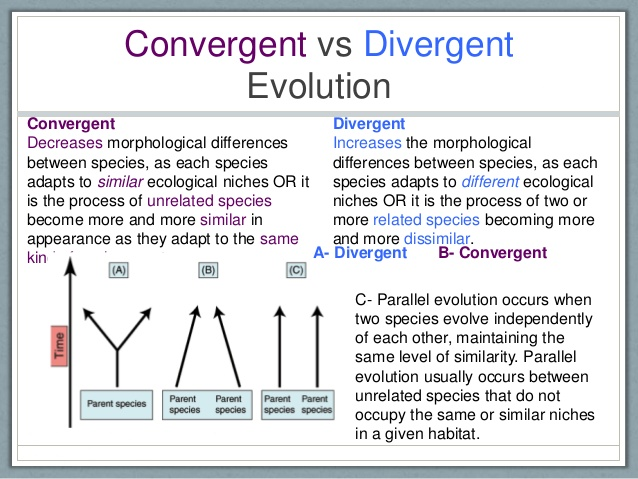
趋同演化(Convergent evolution)和趋异进化(Divergent evolution)
相似不一定同源,但是一般来说同源的必定是相似的
趋同演化(Convergent evolution):Convergent evolution creats analogous structure that have similar form or function, but that are not present in that last common ancestor of those groups
趋异演化(Divergent evolution): the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species, usually a result of diffusion of the same species to different and isolated environments which blocks the gene flow among the distinct populations allowing differential fixation of characteristics through genetic drift and natural selection
趋异演化(Divergent evolution):同一物种不同群体之间累积性差异导致新物种的形成,通常是同一物种扩散后,在不同隔离的环境下通过基因漂流和自然选择,基因分化固定后的结果,也就是说,两个或多个生物学特征具有共同演化起源,源自同一物种,但在演化过程中因环境等自然选择压力的原因,逐渐分化的现象

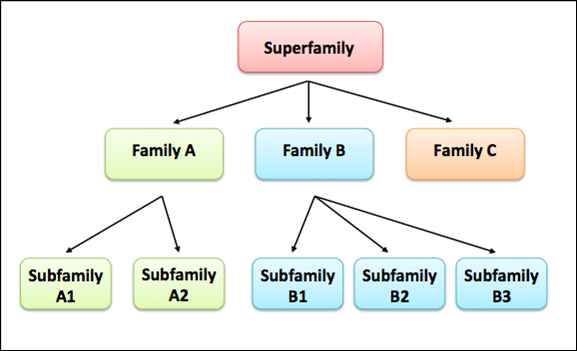
蛋白家族(protein family)和蛋白质超家族(protein superfamilies)
**蛋白家族(protein family)家族有时我们也称为基因家族(gene family),我们一般检索基因家族的时候都是根据数据库比如Pfam来搜索,大多是根据蛋白质氨基酸序列来搜索保守结构域。不同的蛋白质家族(protein family)**又可被归于一个蛋白质超家族
Protein family is a group of evolutionarily-related proteins. In many cases a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 realtionship. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typicallly have similar three-dimensional, functions, and significant sequence similarity
Families are sometimes grouped together into a larger clades called superfamilies based on structured and mechanistic similarity, even if there is no identifiable sequence homology
蛋白质超家族(protein superfamilies):一些蛋白质家族被归入更大的进化分支,基于结构机制的相似性,尽管其没有可确定的显著的序列同源性。简单而言就是蛋白质家族包含了更多进化分支的蛋白,虽然没有同源性,但是因为其结构域或功能基本相似,也被归为一个大类。蛋白质家族的同源关系是可以确定,同源关系上更加严格些